

Last fall, Robert Reich published Saving Capitalism, in which he called for a sweeping realignment of political power to counter the excesses of contemporary capitalism. A realignment has followed, but not the kind Reich had in mind.


If Bill McKibben was not optimistic about the future of the climate movement in the wake of the jarring U.S. presidential election, neither was he particularly sanguine before.

On Election Day, I joined a group of housekeepers at the end of their shifts on a small street behind Le Merigot Hotel, a luxury beachside resort in Santa Monica. These women had decided they wanted a union and announced their desire to vote for one in a National Labor Relations Board election.


The elephant in the room at the presidential debates was climate change. According to a piece in Slate, this year the candidates spent a total of five minutes and 27 seconds on the subject. That’s better than 2012 when candidates didn’t mention it at all.


Thirty miles south of Bismarck, North Dakota, where eroded buttes rise from grassland and corn fields, the Oceti Sakowin camp appears along the winding girth of the Missouri River. Here, a story of protection, protest and cultural conflict unfolds against the desolate prairie.


The future is coming into view. Donald Trump’s victory strengthened the decades-long attack on the role of government. But we’ve got the tools to fight back, and we’re not alone.


Last Wednesday the Drug Policy Alliance, a New York-based drug-reform nonprofit, held a media conference call meant to celebrate a successful election night. Voters in eight states had legalized cannabis for recreational purposes; in several more states ballot measures cleared the way for marijuana’s medical use.
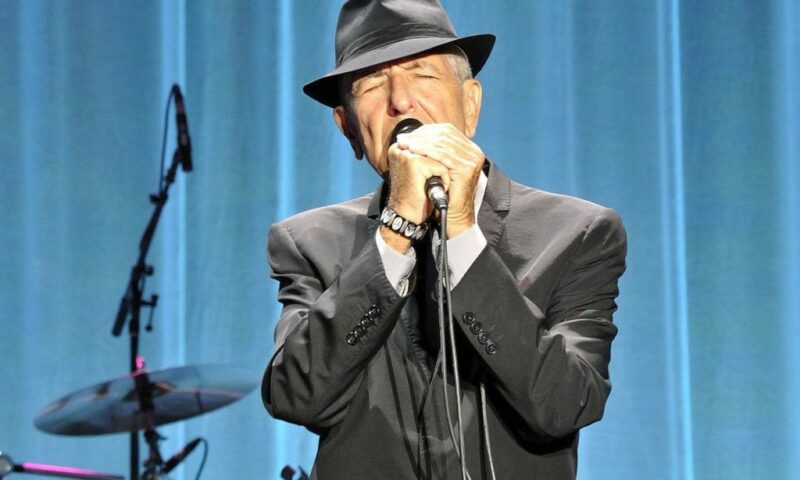


On his recently released final collection of new music, Cohen blamed God for His benighted creatures’ refusal of light: “You want it darker — we put out the flame.” Like, we’re only following orders, Boss. But in another song, Cohen shifted perspective: “Only one of us was real — and that was me.”
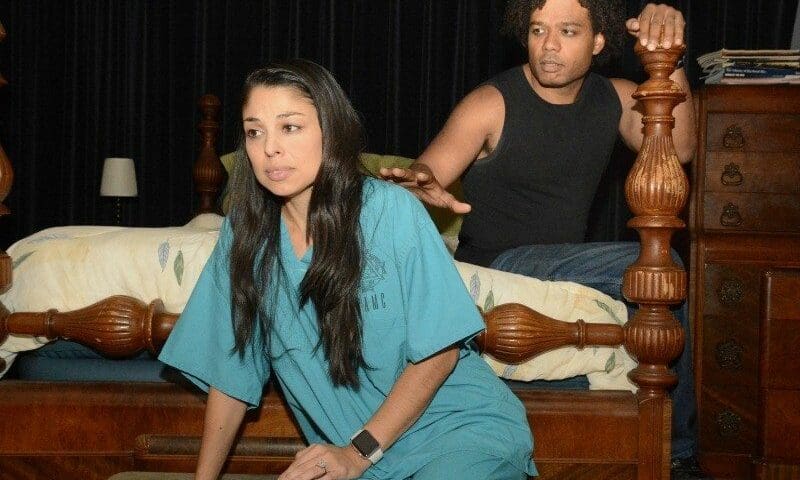


Playwright Rebecca Stahl’s Everything in Between may be a message play, but as such it’s a fundamentally sound one. One of its virtues is the clear picture it furnishes of the kinds of behavior exhibited by sufferers of post-traumatic stress disorder when their illness goes untreated,


One clear winner to emerge from Tuesday’s statewide election was California education. Proposition 55, the wealth-tax initiative, swept to victory with a 62 percent approval margin. Its passage will extend until 2030 Proposition 30’s emergency stabilization funding passed by voters in 2012.